
In today’s ever-evolving healthcare landscape, data analytics has become an indispensable tool for driving improvements in patient care, operational efficiency, and cost management. With the exponential growth of healthcare data and technological advancements, coupled with the increasing need to meet consumer expectations and convenience, analytics plays a pivotal role. It transforms raw data into actionable insights that empower organizations to make informed decisions and optimize operations.
In addition, the critical importance of safeguarding patient privacy and complying with regulatory requirements cannot be overstated. Recent lawsuits against hospitals and health systems are painting that picture very clearly. The revisions to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) guidelines underscore the need for healthcare organizations to correctly navigate data while ensuring strict adherence to privacy regulations effectively ushering in a new future for healthcare data analytics.
In this article, we explore healthcare analytics intricacies, the impact of HIPAA guidelines, and emerging trends reshaping the healthcare landscape, highlighting the positive opportunities they offer.
Understanding Analytics in Healthcare
Healthcare analytics is the use of data to extract valuable insights needed by organizations to help measure various goals and KPIs as well as inform decisions within an organization. By leveraging analytics techniques such as predictive modeling, machine learning, and data visualization, healthcare organizations can unlock the hidden patterns and correlations within their data, leading to better understanding the ROI of their digital initiatives and products.
From electronic health records (EHRs) and medical imaging to wearable devices and telehealth platforms, the increase of digital technologies has resulted in an unprecedented volume and variety of healthcare data and the sources they come from. This wealth of data presents both opportunities and challenges for healthcare organizations. While analytics holds the promise of revolutionizing healthcare delivery, organizations must address various barriers, including data silos, interoperability issues, and data security concerns, to fully realize its potential.
HIPAA Guidelines and Their Impact
HIPAA regulations serve as the cornerstone of patient privacy and data security in the healthcare industry. They aim to enhance the protection of patients’ protected health information (PHI). The evolving revisions introduce stricter requirements for data collection, handling, sharing, and analysis. Healthcare organizations are now tasked in new ways to ensure that their analytics practices and platforms comply with HIPAA regulations. They must safeguard patient privacy to avoid potential legal and reputational risks.
HIPAA guidelines also emphasize the importance of implementing robust security measures. These measures include encryption, access controls, and audit trails. They aim to protect sensitive healthcare data throughout its lifecycle. Furthermore, to keep all of these efforts secure, healthcare organizations should conduct comprehensive risk assessments. They should also adopt privacy-enhancing technologies to mitigate the evolving threats posed by cyberattacks and data breaches.
Examples of PII and PHI
According to the HHS, PHI is “individually identifiable health information, including demographic data.” While the guidelines can be difficult to fully interpret, there are 18 key types of data collected that would be considered PHI identifiers such as:
- Patient names
- IP addresses
- Geographical elements
- Dates related to the health or identity of individuals
- Email addresses
- Social security numbers
- Medical record numbers
- Telephone numbers
- Fax numbers
- Health insurance beneficiary numbers
- Account numbers
- Certificate/license numbers
- Vehicle identifiers
- Device attributes or serial numbers
- Digital identifiers (websites/web pages visited, URLs, IP addresses…)
- Biometric elements, including finger, retinal, and voiceprints
- Photographs of a patient’s face
- Other identifying numbers or codes
A HIPAA violation could occur by using any combination of personal identifying information (PII) with protected health information (PHI). This can happen either explicitly or implied. An example of implied PHI would be a visit to a specific condition page on your website while an explicit example would be a form submission on your website that contains health information.
Balancing Compliance and Innovation
Achieving the right balance between HIPAA compliance and innovation is essential for healthcare organizations. They seek to harness the transformative power of analytics. Ultimately, they aim to deliver a user experience. This experience helps achieve goals and KPIs within the organization. While compliance with regulatory requirements is non-negotiable, organizations must also embrace innovative analytics solutions. These solutions drive improvement and change in healthcare delivery and access to care. By leveraging proper data tracking and collection along with cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and natural language processing (NLP), healthcare organizations can unlock new insights from their data. This leads to more personalized care, proactive interventions, and improved outcomes for patients.
However, innovation must be accompanied by stringent data governance practices and robust security measures. These measures ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of healthcare data. Healthcare organizations should prioritize investments in analytics platforms. These platforms deliver the proper data security technologies to maintain HIPAA compliance. They also foster a culture of innovation and data-driven decision-making.
Exploring Alternative Analytics Platforms
Today, analytics platforms like Google Analytics (GA4) are ill-suited for healthcare due to their inability to ensure HIPAA compliance or sign a Business Associate Agreement (BAA). As a result, healthcare organizations are turning to specialized analytics platforms tailored to their needs and regulatory requirements.
The old method of healthcare data analytics involved having website and user data tracked in GA4 and then reporting out using that information. It was a free tool to use and generally provided the essentials more healthcare organizations needed. However, the days of “free analytics” in healthcare are over and a new dawn has been ushered in, which is one of the more sophisticated data platforms that now come with a cost.
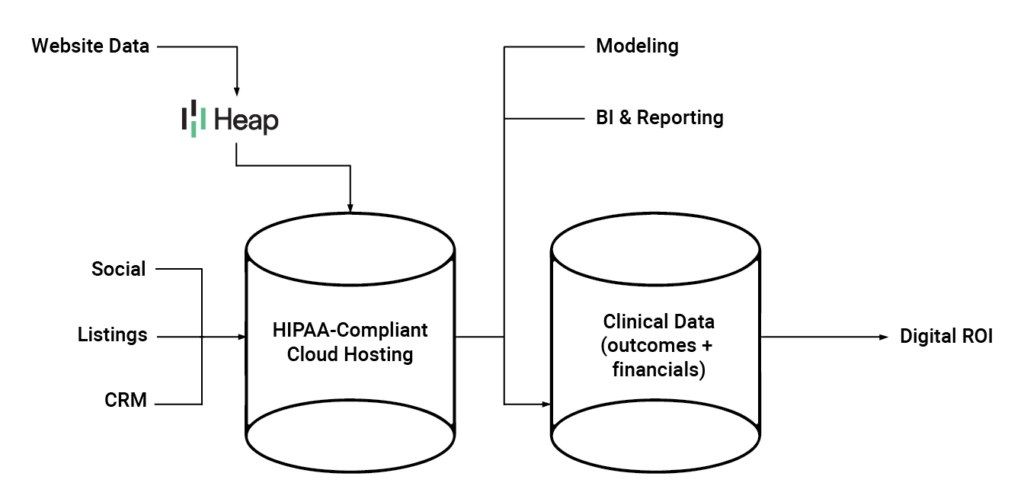
Emerging healthcare analytics platforms such as Heap, Freshpaint, Amplitude, and Adobe Analytics are gaining traction in our space. They offer innovative features and functionalities to meet the evolving needs of healthcare organizations. From data capture and event tracking to visualization and predictive analytics, these platforms enable healthcare organizations to unlock the full potential of their data. They drive meaningful improvements in patient care and organizational performance.

These and many other paid platforms, will sign a BAA and pledge to keep data more secure and compliant. Using Heap as an example, the new method of data collection involves a paid platform sitting between the website and your data warehouse. It essentially “combs” the data to only send through the information you specify. Platforms like Heap also integrate with other popular tools either via the API or built-in native integrations. They still allow you to use conversion tracking tools, such as Google Tag Manager, and visualization tools, like Tableau or Looker Studio.
Modea’s data analytics team is happy to speak to you about your organization’s unique needs for data collection and help you implement the right solution.
Opportunities
While the increase in the cost of analytics is inevitable, it is necessary today. It effectively changes how organizations are using data and the importance they are placing on it. By using a free tool, like GA4, it can be easy to only report on the normal baseline data that is easy to obtain and view. By leveraging paid platforms, organizations are taking a deeper look at how they can leverage these solutions more than before. They extract more impactful data that informs changes and drives future growth.
Many leading healthcare organizations are already harnessing the power of new healthcare data analytics and seeing the rewards of their efforts. A great example is how a health system could leverage analytics to optimize its emergency department operations and reduce patient wait times. By analyzing patient flow data and identifying inefficiencies in the care delivery process, they can implement targeted interventions. These interventions can lead to significant improvements in patient satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Similarly, healthcare organizations could utilize analytics to tailor treatment plans and improve outcomes for cancer patients. By analyzing patient data and clinical outcomes, hospitals could identify personalized treatment strategies that resulted in better outcomes and improved quality of life for patients.
Conclusion
Healthcare analytics holds immense promise for revolutionizing healthcare delivery and improving patient outcomes. However, HIPAA regulations and data privacy requirements dictate that we do it in the right way. Organizations can now implement solutions they are comfortable with and confident will keep them compliant with data and privacy regulations, allowing them to resume tracking meaningful data.
When we look at the power of data and the insights it can provide, the time is now for healthcare organizations to use this information in ways we may have not thought to just a few years ago. Healthcare data analytics has evolved beyond tracking visits, clicks, and conversions. Instead, it is emerging as a pivotal driver in streamlining patient access and enhancing the quality of care they receive.


